Photonic quantum computers
It involves reading the probability distribution, from passing a certain number of single photons through an optical interferometer, with programmable beam-splitter gates.
Readout of the result involves measuring the number of photons in each single photon detector at the output of the system, or in case of a feedback–loop system - in sequential time slots.
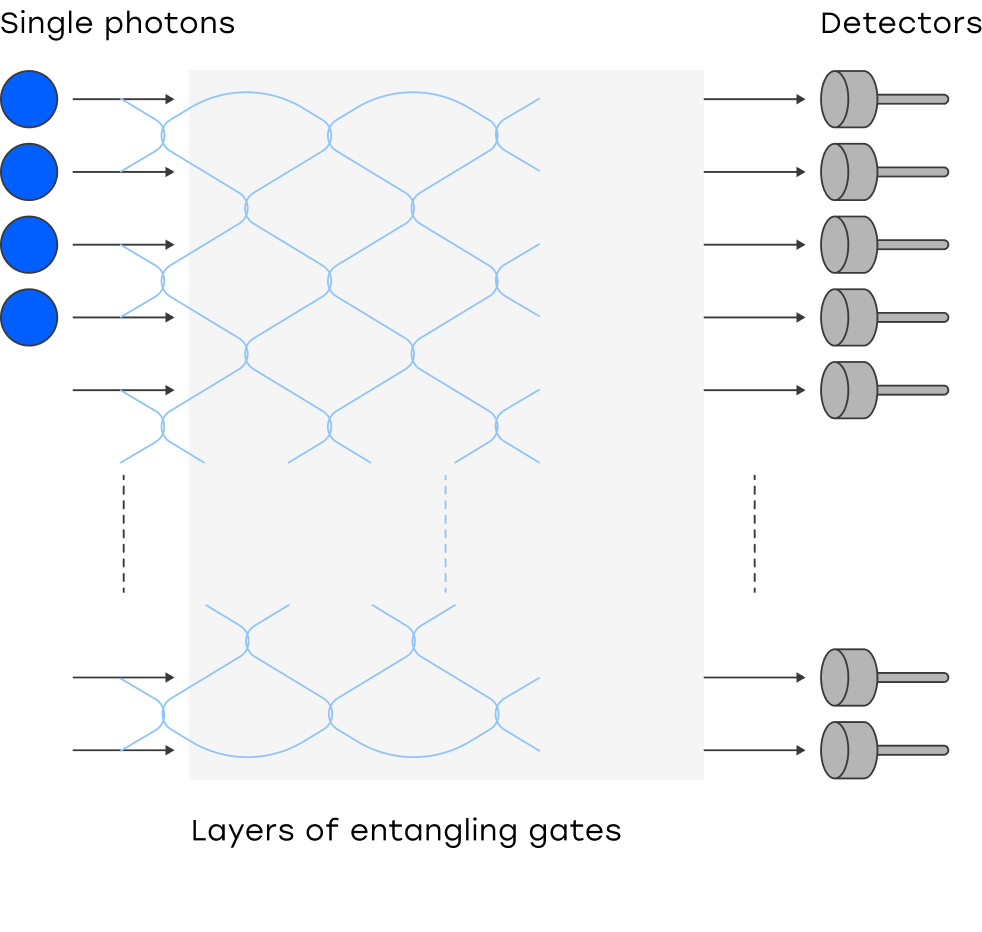
Features of photonic computers
Due to the parallel development of classical photonics - a well-developed industrial sector, quantum computers based on photonic technologies bring a number of highly desirable features, such as:
- ability to perform calculations at room temperature
- ease of maintenance and expansion
- low energy consumption
- scalability - thanks to the ability to add more modules
- the ability to combine into hybrid architectures, thanks to photonics-based quantum communication bands and classical optical fibers
Photonic quantum computer applications
Photonic quantum computers can be applied to many areas in the near future, including those related to medicine, biology or logistics.
Selected applications include:
- machine learning
- classification
- generation
- discrete optimization
- quantum optical memories
ORCA PT-1 systems at PSNC
As part of the EuroHPC PL project, 2 ORCA PT-1 photonic quantum computers have been purchased for PSNC, each with 8 qumodes and 7 programmable parameters in the single loop system. Simultaneously with the delivery, the computers also received an upgrade to the double loop system and will have 14 programmable parameters each.
One of the systems is ready to be upgraded for triple loop installation. The hardware infrastructure of the quantum computer is completed with the purchase of 4 auxiliary computing nodes.


